
Gaining Unauthorized Access to Information
Attackers use a variety of strategies to break into online accounts, devices, and databases, gaining unauthorized access to information. Here are a few commonly used hacking methods: Social Engineering
Social engineering is a type of manipulation in which attackers trick people into doing something dangerous or damaging. In the context of hacking, this could involve convincing someone to disclose login credentials, download malicious software, or reveal some other sensitive information. Social engineering is achieved through a number of ways, such as impersonating a trusted company, coworker, or authority figure; promising some kind of reward, usually monetary; or creating an urgent situation. For example, victims might receive a false notice that their account on a trusted site has been hacked, along with a link to fix the issue. The link will lead to a fake version of the website, which will ask the victim to log in and then record all of their inputted information. Viruses and Malware
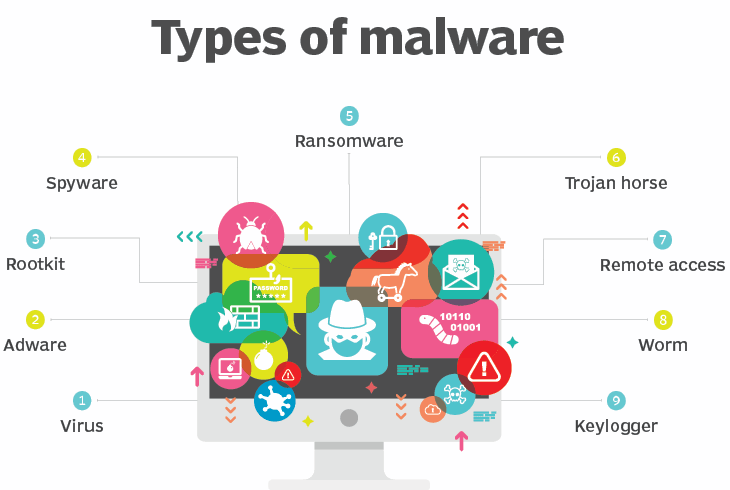
Malware is malicious software that, when downloaded on a device, can steal data, change/destroy operating systems, or spy on user activity. It can infect devices through the downloading of seemingly innocent files and applications, the viewing of malicious ads, or manipulation via social engineering. Common types of malware include viruses, which duplicate themselves and spread by attaching to other programs; Trojans, which hide inside seemingly innocent programs so that victims are tricked into downloading them; spyware, which spies on device activity; worms, which can autonomously replicate and spread across systems, and more.
This is a method commonly used to hack databases without strong security. Attackers manipulate SQL queries that are sent to retrieve information from a database, thus gaining access to potentially hidden data. Successful attacks carried out using SQL injection can result in the leakage of information such as passwords and personal information.